The grid-connected inverter is a special inverter whose output AC power can be synchronized with the frequency and
phase of the mains power, so the output AC power can be returned to the mains power. The inverter can adapt to
various harsh environments and apply in residences, factories and ground-mounted power stations. As an interface
device between photovoltaic cells and the grid, the grid-connected inverter converts the electric energy generated
by the photovoltaic cells into alternating current and transmits it to the grid, playing a vital role in the
photovoltaic grid-connected
power generation
system.
Installation of On Grid Inverter
Step 1:
Choose a ventilated and sun-protected location to facilitate heat dissipation and maintenance. Depending on the
placement direction of the grid-connected inverter, you can choose an installation location facing east or west to
make full use of solar energy. Ensure that the grid-connected inverter maintains a certain safe distance from
surrounding objects to avoid overheating or collision.
Step 2:
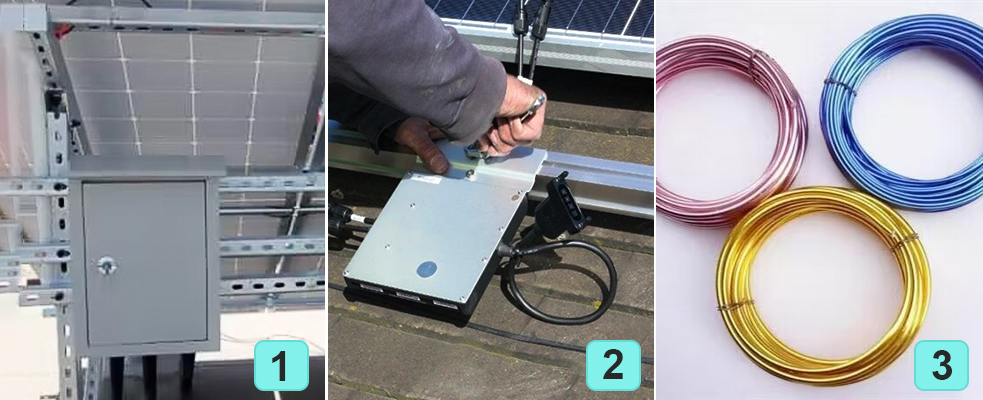
Connect the solar panels, load, grid, etc. to the corresponding terminals of the grid-tied inverter according to
the attached wiring diagram. Make sure the wiring is correct and secure. Use the included fixing device to fix the
grid-connected inverter in the selected position to ensure stability and no shaking.
Step 3:
Connect the power cord of the on grid-connected inverter to the power grid to ensure that the power supply is
normal.
Customer says
“ So happy to work with EnterSolar. Innovative on grid inverter
design and customization make us feel good. And the inverter good quality and reliable performance are
really nice. The grid-tied inverter supplied is so much easier to install, and offers more features than any
other.
”
- - - by Barron Alan- - -
On Grid Inverter FAQ
Can on-grid solar system work without batteries?
Yes, on-grid solar systems can operate without batteries. These systems, also known as grid-tied or
grid-connected pv systems, are designed to generate electricity from solar panels and feed it directly
into the utility grid. When the solar panels produce more electricity than the home or business consumes,
the excess power is sent back to the grid. Conversely, when the panels aren't producing enough power
(e.g., at night or on cloudy days), electricity is drawn from the grid.
Batteries are optional components in these setups. They are used to store excess solar energy for use
during periods of low or no solar generation, providing backup power during grid outages. However, without
batteries, the system relies solely on the grid for balancing energy supply and demand. This can be
cost-effective for grid-connected locations with reliable power supplies but may leave the user without
electricity during blackouts. The decision to include batteries depends on individual needs, budget, and
energy resilience goals.
Can on-grid solar inverters store excess energy?
On-grid solar inverters are not designed to store excess energy. Their primary function is to convert the
direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that
can be used in your home or sent back to the grid. Any excess energy generated by the solar panels is
typically fed back into the electrical grid, allowing you to earn credits or compensation through net
metering or feed-in tariffs, depending on your location.
To store excess energy for later use, you would need a separate energy storage system, such as a battery.
Energy storage systems like lithium-ion batteries can capture surplus energy during sunny periods and
discharge it when your pv panels are not producing electricity, like at night or during cloudy days. These
systems offer greater energy independence and allow homeowners to utilize their solar power even when the
sun isn't shining.
What is the difference between on-grid and off-grid solar inverter?
On-grid and off-grid solar inverters serve different purposes in solar power systems.
Grid tied solar inverters are designed to work in conjunction with the utility grid. They convert the DC
electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity that matches the grid's voltage and frequency.
These inverters allow excess energy to be fed back into the grid, earning credits or compensation through
net metering. They do not provide power during grid outages, as they are dependent on a functioning grid
connection.
Off grid solar inverters are used in systems that are not connected to the utility grid. They store excess
energy in batteries for use when the sun isn't shining, providing a reliable power source in remote areas
or during power outages. Off-grid inverters must manage the entire power supply, making them more complex
and often requiring additional components like charge controllers and battery systems.
In summary, on grid inverters are grid-dependent and promote grid integration, while off-grid inverters
are self-sufficient, providing energy independence in isolated locations.
How does an on-grid solar inverter connect to the electrical grid?
An on grid solar inverter connects to the electrical grid to efficiently convert and synchronize the
direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used
in homes and sent back to the grid. The process involves several key steps:
1. DC to AC Conversion. Solar panels generate DC electricity, and the inverter's primary function is to
convert this DC power into AC power, which is what the grid operates on.
2. Synchronization. The inverter ensures that the AC power it produces is synchronized with the grid's
frequency and voltage. This synchronization is crucial for safe and efficient grid
interaction.
3. Anti-Islanding Protection. Inverters have anti-islanding protection mechanisms to prevent them from
sending power to the grid during grid outages. This protects utility workers and maintains grid
stability.
4. Grid Connection. The inverter is connected to the home's electrical panel and, through that, to the
grid. It monitors the grid's conditions and feeds excess energy back into the grid when the solar system
generates more power than the home consumes.
How is the output of an on-grid solar inverter measured?
The output of an on-grid solar inverter is typically measured in several key parameters, with the primary
ones being:
1. AC Power Output. This is the most critical measurement and is usually expressed in kilowatts (kW) or
megawatts (MW). It represents the amount of electrical power the inverter converts from the direct current
(DC) generated by the solar panels to alternating current (AC) that can be used in your home or fed back
into the grid.
2. Efficiency. Inverter efficiency indicates how effectively it converts DC power into AC power. It's
expressed as a percentage, and higher efficiency means less power loss during the conversion
process.
Monitoring systems and utility meters often display these parameters, allowing homeowners and grid
operators to assess the performance and contribution of solar installations to the grid.
Related Solar Products

A hybrid inverter is a solar inverter with a built-in charge controller. It can also be a machine
combination of on/off-grid inverter.

The biggest feature of the grid-tied inverter is its great system power, used in renewable energy power
generation without battery storage.

A foldable solar panel is a compact and flexible photovoltaic module designed for portability. It can be
easily folded for transport or storage.